Received: August 19, 2011
Accepted: October 21, 2011
Ref: Jain A, Sharma V, Patra SK, Goel A, Sherwal BL. Evaluation of nested Polymerase Chain Reaction targeting hup B gene in the diagnosis of tubercular ascites. Internet J Med Update. 2012 Jul;7(2):9-13.
EVALUATION OF NESTED POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION TARGETING HUP B GENE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULAR ASCITES
Anju Jain*, Vivekanand Sharma**, Surajeet Kumar Patra***, Atul Goel† and B L Sherwal‡
*Director Professor, **Resident, ***Senior Resident, Department of Biochemistry,
†Professor, Department of Medicine, ‡Director Professor, Department of Microbiology,
Lady Hardinge Medical College and associated hospitals, New Delhi, India
(Corresponding Author: Professor Anju Jain, Director, Department of Biochemistry, Lady Hardinge Medical College and associated hospitals, New Delhi, India; Phone: 01123408149; Email: dranjujain@rediffmail.com)
ABSTRACT
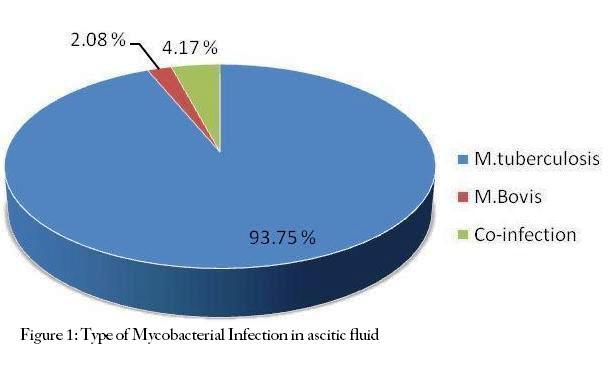
Abdominal tuberculosis usually has nonspecific presentation, frequently mimicking other diseases. Because of the limitations of the conventional methods of diagnosis of extra pulmonary tuberculosis, focus is shifted to molecular methods. The objectives of this study are to evaluate the role of nested Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) targeting hup B gene as a rapid diagnostic modality of tubercular ascites and also to detect the infecting species (Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis). 100 suspected tubercular ascites patients were enrolled in the study. Ascitic fluid was processed by Universal Sample Processing (USP) method and two steps nested PCR was performed targeting hup B gene. Patients were put on Anti Tubercular Therapy [Category I, (2 HRZE + 4 HR) 3, RNTCP, India]. A positive response to therapy was considered as gold standard and PCR assay was compared to determine sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value in diagnosis of tubercular ascites. 79 patients could be followed up to see the response to therapy. Of these, 39 were PCR positive and 35 responded to Anti Tubercular therapy. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value were found to be 97.1%, 88.6%, 87.2% and 97.5% respectively. The good sensitivity and specificity obtained in the study suggests the use of PCR targeting hup B gene as a routine diagnostic tool for tubercular ascites. Another added advantage is the ability to identify between M. tuberculosis and M. bovis which otherwise have similar clinical presentation.
KEY WORDS: Hup B gene; M. tuberculosis; M. bovis; Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction
 |
|---|